A computed tomography (CT) scan is a diagnostic tool used to create detailed images of various parts of the body. With it, doctors can see bones and soft tissue. Scanning almost any part of the body and using it to diagnose a variety of medical conditions including cancer and more.
There is radiation exposure, so if you are pregnant or suspect you might be pregnant, please speak with your doctor before the exam.
However, due to the radiation involved, it is essential that certain precautions need to follow to keep both patients and healthcare professionals safe.
Why CT scan is done?
The CT scan helps to identify and monitor the various medical conditions or issues in the body. It provides more detail than the X-Ray Machine. There is movement of the beam in a circular motion, which allows capturing of more detailed images of the single organ from different angles.
Also help diagnose tumors, and internal bleeding, or check for other internal injuries or damage and for a tissue or fluid biopsy. It shows detailed images of bones, muscles, fat, organs, and blood vessel.

CT Scans with Contrast
Sometimes the CT scan is with the contrast. Contrast is defined as the substance that is taken orally through the mouth or injected into the IV line. It causes the particular organ or tissue to study and see clearly.
In case of a recent illness severe or moderate or any kind of allergy, you must inform the doctor before the exam. The Seafood allergy is not considered to be a contra-indication for the iodinated contrast, as reported.
What to know before your exam?
- The CT scan will last for approximately 15 minutes, but it completely depends on the type of scan.
- If the scan is with the Contrast, make sure not to eat or drink 4 hours before your exam.
- Always discuss the exam with your doctor regarding the pre-exam effects and precautions and the post-exam effects.
Precautions need to be taken during the exam
- All patients (and visitors) must wear protective clothing such as lead aprons that shield them from radiation exposure.
- The shielding material will depend on which type of scan has been requested by their doctor.
- No metal objects (such as jewelry or watches) inside the room.
- These could interfere with the machine’s readings and make it difficult for the radiologist to interpret results correctly.
- Shoes should also not contain any metallic components, such as iron inserts because they could potentially block part of your body from being scanned accurately enough.
- It is advisable to remove all electronic devices – including cell phones.
- Patients should always inform their doctor/radiologist about any metal fragments inside the body.
- Including dental fillings or thick scar sections along their chest because the phase affected is left unnoticed.
- It is important for patients to inform their physician if they are pregnant since X-ray exposure could harm developing embryos and fetuses.
- Certain medications interact negatively with radiation exposure, so ensure your doctor has been informed about all current medicines.
- Diabetic People: They can eat a light breakfast or lunch prior 3 hours before the exam. Discontinuation of your medication for 3-4 hours. The doctor will give detailed instructions.
During the Scan
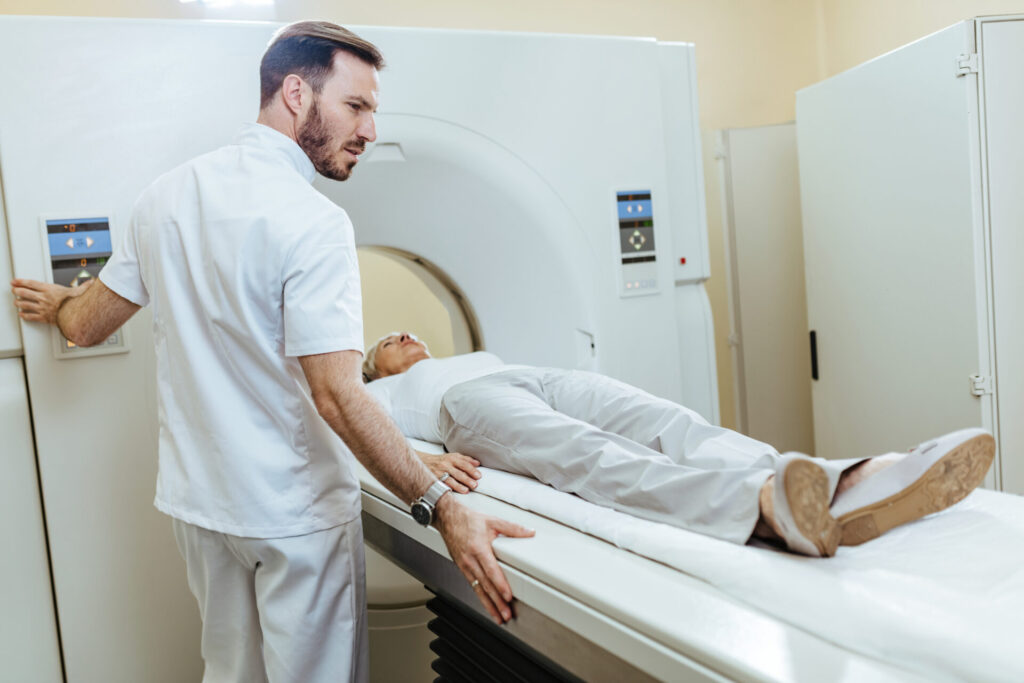
- You will lie on the scan table that slides into the large circular opening of the CT Scan Machine.
- CT Scanner will begin to rotate around the body, and the X-rays will pass through the body. During this, you will hear a clicking sound.
- The computer will absorb and transmit the X-rays and will transform the information into images; interpreted by radiologists.
- It is important to remain still during the procedure to monitor clear images.
After the Scan
- If you have taken the contrast media, they may monitor you for some period of time for any side effects or reactions like itching, rashes, or any.
- There is no special type of care needed after the scan, you can resume the activities and diet if your doctor doesn’t advise you differently.
Taking precautionary measures helps keep both personnel operating as well as patients receiving treatments safe from potential radiative harms caused due to incidence direct contact or inappropriate usage practices.
Ensuring those involved do indeed adhere to strictly prescribed protocols governing these powerful pieces of medical technology will go far in protecting the long-term well-being of those impacted by their users alike.
CT Scan Machine Handling
It is an important part of medical care as they help identify illnesses and provide doctors with detailed images of the body. If you handle them improperly, however, it can lead to complications for patients or even worse.
Handling a CT scan machine can be daunting for many. If done properly, it is important to take steps to ensure that the patient and provider are safe. It should include proper cleaning and disinfection of devices between use. Also, wearing protective garments such as lab jackets or gowns during scans, and observing the safety signals present on the device itself at all times.
Before scanning, operators need to thoroughly understand the working process through manuals and regular practice sessions.
They must also follow all directives given in order to make sure no damage occurs due to their negligence or lack of knowledge about how this machine works. In this article, we will explore how to correctly handle a CT scan machine in order to get accurate results while protecting.
Here are some tips on how to properly handle a CT Scan machine: –
Read the Manual Carefully
The owner’s manual of the CT scanner should include step-by-step instructions on how to set up and operate it safely. Make sure that you read through the manufacturer’s manual on how to properly operate the machine before attempting anything.
You must thoroughly read the manual to know exactly what steps to follow when operating it safely, including power-off sequences, etc. Also, take some time familiarizing yourself by looking at diagrams showing where each switch should go when doing various scans or operations.
Proper Movement
Be sure to take appropriate safety measures, such as using transport trolleys, when moving any part or component (e.g., gantry) of the scanner or transporting entire scanners.
Never move components around roughly or without proper equipment; this could potentially damage sensitive parts involved in scanning processes.
Prepare properly
Ensure that all parts of the scanner are properly connected and calibrated before beginning your session. You should also make sure that all seating or standing surfaces are secure for patients undergoing scans. Also, adjust dressings accordingly so items such as metal zippers won’t impact results during scanning processes.
Protective Gear
Operators should always wear protective gear such as rubber gloves, and goggles/visors during scanning sessions. Since radiation exposure from X-rays may occur inadvertently while handling components that have not been adequately shielded.
Unintended discharge may take place due to sources like defective isolations etc… Use lead aprons when operating close-range recording systems inside tunnels too!
Powering On & Off Procedures
Mastering specific powering-off protocols ensures scans take place under controlled pre-imaging conditions. Alertness reduces false readings due to inhibited functionality during active runs.
Logging functional entry upon each session greatly facilitates future troubleshooting efforts too! Scheduling Processes implement proper scheduling techniques allowing optimal scanning sessions with minimal impairment.
Watch out for Warnings and Alerts
Ensure alarms appear correctly intended objectives & solutions show no inconsistencies between screen displays & stored information. Immediately abort reloading if discrepancies are found anywhere, and refer back to manufacturer guidelines for assistance with encountered procedures.
Benefits of properly Handling Machine
Aside from ensuring accuracy in diagnosis for ill people seeking treatment using technology-related devices like these, following guidelines/ procedures provided within the user’s handbook deriving direct benefits include
1. Reduced Radiation Exposure
– Proper maintenance leads to a reduced amount of exposure. One would receive events working in close proximity due to repeated testing protocols conducted throughout the duration of case studies.
2. Improved Precision
– By utilizing correct techniques manipulating the focused beam along its axis combined with regulating motor speeds automatically. Scanners successfully find the best refinement applicable to image quality output.
Handling a CT scan machine requires in-depth knowledge about its various aspects from setup through radiation exposure requirements. Alongside good communication skills amongst operators & clients ensuring everything runs smoothly throughout examinations.
Beyond understanding common interface features along experimental techniques careful attention needs to be put towards safeguarding people against potential health hazards & damage posed by prolonged unattended usage.
Dos for Machine Handling
- Wear protective clothing when handling the equipment including gloves, goggles, and lab coat in order to protect yourself from radiation exposure
- Follow manufacturer instructions carefully
- Thoroughly inspect all wires before using the equipment
- Maintain regular maintenance according to company protocol
Don’ts
- Not to attempt repairs without proper training
- Don´t touch internal components while operating
- Also, do not forget that practice makes perfect – spending time regularly familiarizing oneself with best practices can ensure safe use.
Importance of Radiation Jackets
Computed Tomography (CT) Or Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT) scan is a diagnostic tool that identifies and monitors the diseases inside the body. It creates detailed images or scans of the body.
Modern CT machines are more advanced and fast, produce better quality 3D images of the areas inside the body, and also detect abnormalities better. It is widely used to diagnose cancer, circulatory diseases, coronary artery diseases, blood clots, and almost every area of the body.
During the CT scan, there is radiation exposure, it uses X-Rays, which are a form of ionizing radiation. Exposure to Ionizing Radiation increases the risk of cancer.
What is Radiation?

Radiation is the emission of energy in the form of waves or particles which travel through space carrying with them electromagnetic energy.
It can be natural, where it occurs in nature and has no effect on humans or other living organisms, or artificial such as an imaging machine produces radiation.
Radiation plays an important role in many scientific fields including medical imaging, astronomy research, and astrophysics. Additionally, it has numerous applications in engineering disciplines such as welding and industrial radiography.
Types of Radiation: Ionizing & Non-Ionizing
Ionization occurs when electrons become separated from their atom’s nucleus. It creates ions that can damage molecules in living organisms causing DNA mutations and cellular damage including cancerous cells.
Most forms of non-ionizing radiation do not have enough energy to break apart atoms reliably into ions. Government agencies such as OSHA (Occupational Safety & Health Administration) monitor safety hazards that they pose.
Radiation Exposure
Everyone exposed to some kind of exposure whether in natural form or artificial form. We are regularly exposed to various kinds of radiation like radioactive materials. It includes radon a radioactive gas that comes from the natural breakdown of the uranium in soil, water, rocks, and building blocks, and cosmic rays from outer space; known as background radiation.
Background radiation varies from country to country. The largest source of this is radon which is typically about 2 mSv per year, a natural gas found in our homes. Location is also important, being at a higher altitude increases a person’s exposure.
The average radiation one should take is 3 millisieverts per year(mSv).
Radiation from CT scan machines is ionizing radiation, including X-rays, Cosmic rays, and radiation from radioactive materials. Depending on how many slices and how much detail we need, these machines vary the amount of radiation used.
Risks with the Radiation Exposure
However, there are risks involved with using a CT scan. Exposure to these high levels of radiation can potentially have long-term physical health effects on individuals who use them too often.
Modern scanners keep patient doses as low as possible. Medical professionals should regularly monitor the level of doses to ensure the safety of patients.
Experiencing some amount of radiation is unavoidable during such scan treatments. Preventive measures like proper shielding materials, controlling on/off times, and monitoring patient dosages can help that risks from these devices are kept to an absolute minimum.
Most medical uses of radiology produce small doses of ionizing radiation. It is important to be aware of this potential risk factor associated with CT scanning. Also, talk about risks and precautions with your health professional before undergoing any test.
At very high doses, the radiation can damage the functioning of the tissues and organs and also causes nausea, vomiting, and radiation burn. Excessive exposure to radiation doses can increase the risk of various types of cancer.
Nuclear emergencies can release radioactive iodine, which can increase the risk of Thyroid Cancer if breathed in or taken in. It is important for children as well as adults to take precautions.
Radiation Jackets

They are an important form of protection against radiation exposure. It serves to protect individuals from exposure by blocking or shielding them from dangerous amounts of radiation-causing particles or rays, such as X-rays and gamma rays.
Reduce or even completely eliminate any potential radiation-related illnesses by providing a barrier between the person and the source of radioactive material in their environment.
Various protective layers inside them absorb most forms of harmful radioactive particles coming into contact with their wearers’ body surfaces when they design these specialized garments.
Thus, ensuring an effective level of safety for those handling such materials or entering areas where higher levels may be present.
Radiation Jackets importance
By wearing a radiation jacket, people can properly protect themselves when working with materials that may contain harmful amounts of radiation and potentially extend their lives.
The importance of radiation jackets lies in their ability to shield individuals while allowing them access to areas with potentially high levels of ionizing or non-ionizing electromagnetic fields. Its features include lightweight breathable materials, adjustable straps for ease of movement, and an airtight seal that keeps out external elements like dust particles.
A radiation jacket provides protection against harm while allowing maximum freedom and mobility without compromising safety standards. It comes with features such as adjustable straps and collars that make them comfortable to wear for long periods of time while still providing excellent levels of protection from harmful X-ray or Gamma ray radiation sources.
Users shall use appropriate radiation protection devices such as barriers, aprons, goggles, and thyroid shields during the operation of X-ray equipment. Verify these devices periodically for their shielding adequacy.
Radiation Protection Shielding
- Lead Apron- 0.25mm Lead Eqv
- Rubber hanging Flaps (In IR )- 0.5 mm Lead Eqv
- Hand Gloves – 0.25 mm Lead Eqv
- Lead Glass window- 2 mm Lead Eqv
- Mobile Protective Barrier (MPB)- 1.5 mm Lead Eqv
- Thyroid Shield -0.25 mm Lead Eqv
- Gonads Shield- 0.25 mm Lead Eqv
- Eye Wear (Shield)- 0.25 mm Lead Eqv
- Door (Lead Lined)-1.7 mm Lead Eqv
Manufacturers produce radiation shielding materials from LEAD. Various applications including imaging, radiation therapy, and industrial shielding often use it. They use X-rays attenuating garments such as aprons, skirts, and vests
People cannot wear lead as apparel unless it is in wearable form. Use of Mix binders and additives with lead to transform it into wearable material and make flexible lead vinyl sheets.
After that, Tailoring of sheets to desired thickness to achieve the required lead and incorporate it into the radiation shielding garment. The Three standard levels of equivalency for garments are 0.25mm, 0.35mm, and 0.5mm.
- Lead Aprons can effectively attenuate certain kinds of radiation due to their high density and high atomic number. Effective in stopping X-rays and Gamma rays.
- Aprons are of 0.5mm thickness and have been shown to shield approximately 99% of the potential radiation dose.
- They must cover the front body from throat to knees, back from shoulder to the below of Buttocks
- Special Aprons contain elements of Barium and Iodine in combination with lead and plastic struts providing protection from lead.
- One can reduce the weight of the apron, thus reducing the stress over the shoulder and spine and enables to use for a longer procedure.
- As the lead gown does not cover the neck, the consistent neglect of the matter of thyroid shield is a matter of concern.
- Exposure to radiation over many years can develop Thyroid Carcinoma. The Thyroid shield can decrease the amount of effective dose 2.5 fold and almost 50% reduction in total exposure.
In Conclusion,
Safety precautions in the CT scan room are of utmost importance to minimize radiation exposure. The use of radiation jackets provides an additional layer of protection for both patients and medical professionals.
By adhering to these precautions, the risk associated with radiation exposure can be significantly reduced. Remember, the well-being and safety of individuals should always remain a top priority in any healthcare setting.

