MRI stands for Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
It is a type of scan that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the human body. Doctors can use MRI scans to observe organs, tissues, joints, and other parts in great detail without using ionizing radiation.
MRI works by spinning protons at a very high speed in a magnetic field which produces electrical signals sent to a computer that then creates an image or multiple images (3D) from these signals.

We can use conventional X-rays to provide detailed views of areas to diagnose diseases or injuries, and also for the areas that could not see. It also enables physicians to detect abnormalities earlier than any other method available today.
This is how MRI scans enable doctors and radiologists to detect issues like cancer since they more clearly show what’s happening within our bodies.
How does the MRI Work?
Doctors use a large magnet and radio waves to provide detailed images of organs and other hard-to-see structures in the body during an MRI scan.
- The patient will lie on a table that slides into a tube that houses coils that generate magnetic fields around them.
- As pulses of energy pass through within these coils, hydrogen atoms located in different tissues release tiny echoes picked up by receptors situated within special resonating chambers.
- These echoes can convert digital data displaying cross-sectional views detailing internal features.
- It helps doctors diagnose conditions like cancer or neurological disorders accurately and with precision accuracy.
- By using advanced techniques such as contrast enhancement, these scans provide detailed information about various organs within the body.
- MRI does not involve any kind of radiation exposure like other forms do making it less hazardous in comparison.
Why do it?
MRI is a non-invasive procedure used to produce detailed images of the body’s organs and tissues. It works by using powerful magnetic fields, strong radio waves, and state-of-the-art computer technology to generate high-resolution 3D images.
There are many reasons why an individual may need to receive an MRI scan. They check fractures or tumors in bones and joints. Diagnosing various neurological diseases such as multiple sclerosis, and tracking progress after recent surgeries/injuries.
This makes it an especially useful diagnostic tool for identifying diseases quickly. Doctors use MRI scans for diagnosis, planning treatments, and monitoring disease progression or response to treatment.
Creating clear pictures from these signals shared back with radiologists and medical professionals can more accurately diagnose conditions such as cancer or muscle injuries quickly and safely.
When to do the MRI?
The MRI Scan is a non-invasive tool used to detect illnesses inside the body that affects the soft tissues. It includes-
- Brain aneurysms, tumor
- Cysts, and nerve tissues
- Injured or damaged ligaments
- Spine Injuries and Spinal Cord,
- Pelvic Organs, Reproductive organs, Digestive organs
- Organs in the chest and abdomen, including the liver, kidney, spleen
- Multiple Sclerosis, Breast Cancer, etc
For Heart
- To evaluate and diagnose cardiovascular conditions, the functioning of the heart valves, and chambers.
- The infection and the blood flow in the heart
- Effects and the Risks of Cardiac Diseases
For Body
- Tumors or clots in chest or abdominal sections
- Liver and bile diseases
- Inflammatory conditions
- Defects and inflammation in blood vessels.
For Bones and Joints
- Infections and tumors
- Damaged Joints/ Bones
Sometimes doctors use mammography to detect breast cancer.
Types of MRI Scans
MRI is a specialized kind of imaging scan used for diagnosis. There are many different types, designed to achieve specific outcomes and provide unique insights into the body’s functioning or anatomy.
There are many types of MRI including functional, cardiac, breast, Magnetic Resonance Angiography, and Magnetic Resonance Venography.
Functional MRI
It is an imaging technique used to measure the activity of various areas in the brain. fMRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of organs and tissues within the body, including those in the brain.
fMRI measures changes related to blood flow which reflects oxygen consumption and overall metabolic patterns of active areas of the brain. This imaging tool provides valuable information about cognitive functioning.
Over the past few decades, it has revolutionized neuroscience research, by helping to map out patterns of the brain. One can use it to address memory loss or map out particular regions during surgery.
The usage of fMRI has allowed us to have an insight into the working process within our minds, making it easier to diagnose issues. It helps to improve drugs that would aid sufferers who suffer from conditions like autism or depression.
Today it’s being used not only for scientific applications but also for medical purposes such as diagnosis and treatment of neurological disorders.
Cardiac MRI
It is a type of imaging technique used for assessing and visualizing the structure, physiology, pathology, function, and blood flow of the heart. Helps to show the structures and functions of the heart, arteries, valves, and vessels.
Cardiac MRI can diagnose various conditions including atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure. Also includes, congenital cardiovascular diseases, syndromes involving coronary artery blockage, and certain valve abnormalities.
The information obtained from this procedure is essential in providing reliable data on which doctors base their treatment decisions without any further invasive testing being required.
Cardiac MRI not only provides more accurate results than other technologies but it also has very low risks associated with it.
Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)
It is a non-invasive imaging technique used to look at blood vessels and blood flow. MRA uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves, and computer technology to produce images of body structures with good qualities that can be used for diagnosis and treatment purposes.
MRA works by injecting a contrast material into the patient’s bloodstream which helps improve the quality of images produced from magnet resonance angiographies. We can see details about important elements such as obstructions or narrowing in arteries.
The clarity offered by scans makes it very helpful in diagnosing various types of vascular diseases. A CT Angiogram exposes radiation, MRA does not use radiation.
Magnetic Resonance Venography (MRV)
It is a non-invasive imaging technique that allows for the visualization and evaluation of veins in the body. MRV uses MRI technology to create detailed images of blood vessels and vein-related conditions such as deep vein thrombosis or varicose veins.
Scientists can use MRV to help better understand how diseases affect the circulatory system for research purposes. It is primarily used to diagnose vein abnormalities or anomalies due to blood clots, clotting disorders, or other blockages that may be causing decreased circulation.
MRV can help diagnose vein disorders more accurately to evaluate the flow direction and size changes in post-operative junction sites.
Breast MRI
It is an imaging technique used to detect potential abnormalities and cancer in the breast. Allows to take detailed images of a woman’s breast, allowing doctors to better diagnose issues that may appear.
Offers to see abnormalities such as lumps, thickening of breast tissue, changes to skin texture around the nipples, and discharge from the nipple. The machine itself does not involve exposure to radiation and the procedure takes 40-60 minutes without discomfort or pain around the nipples.
This allows doctors to get a better understanding of ongoing conditions within the breast tissue. Early detection is key when it comes to managing this form of cancer but unfortunately, there are no certainties about what causes it and how best to identify symptoms.
Types of MRI machines
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an imaging technique that uses magnetism, radio waves, and a computer to create detailed images of the body. It has been used to diagnose diseases such as cancer, heart disease, stroke, multiple sclerosis, and liver disorders.
They can use them to identify problems with bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments and detect various disease processes. MRI can also detect tumors or other abnormalities in certain organs or tissues. Doctors often use these high-resolution scans when diagnosing medical conditions.
MRI machines are of various types:
Open MRI Machines
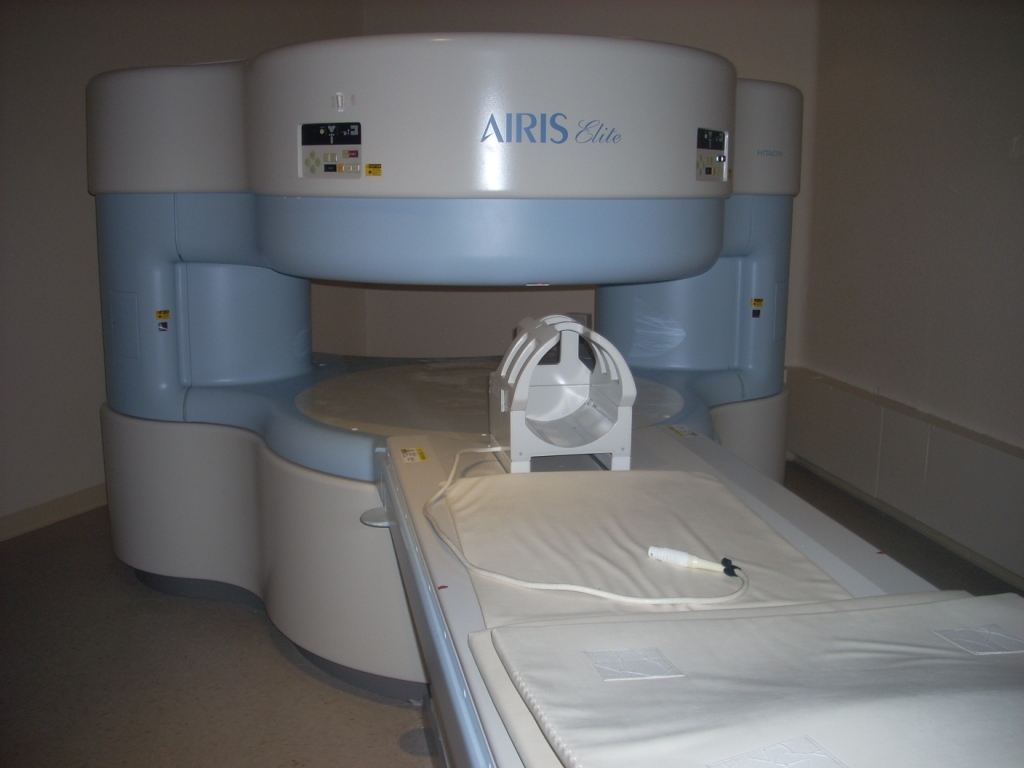
These machines are exactly what they sound like. An Open MRI consists of two large magnets placed on top and bottom that allow one to view internal body structures with greater precision. It’s an alternative to traditional, closed MRIs which require patients to lie within a confined space for their scan.
They make it the more comfortable option by not enclosing the patient in any form. This makes Open MRI particularly helpful when dealing with patients who have physical limitations or other such as Claustrophobia.
It helps to get scans done quickly without feeling overwhelmed by being inside an enclosed space. New advancements such as high-field strength systems and 3T scanners with dynamic capabilities, and superior diagnostic data help deliver diagnosis accuracy.
Pros
Open MRI has become a popular choice for those looking to get diagnostic imaging, due to its several advantages.
- One notable benefit of an open MRI is that it is more child-friendly.
- They are typically quieter and provide more comfort for the patient.
- Advanced technology with higher-resolution images allows doctors to detect even slight changes in the body’s condition.
- Also offers scanning in a standing position.
- Fewer Side effects, fewer artifacts, and Cost less.
Cons
- Not ideal for all bodies
- Longer scan times
- It uses low-field magnets that result in low-quality imaging.
Closed Bore MRI
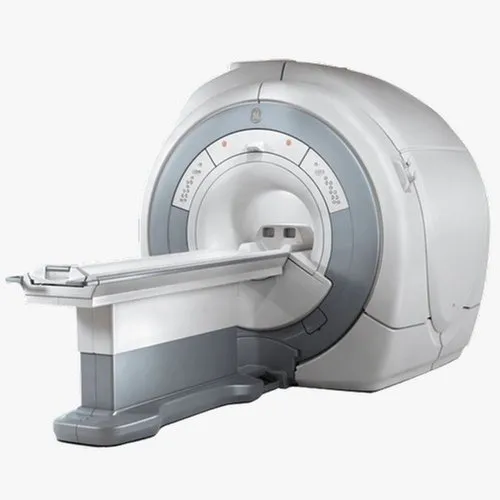
A closed-bore MRI machine refers to a traditional MRI system with a cylindrical-shaped magnet, providing a tunnel-like structure for the patient to lie inside during the scanning process. The bore, or the opening of the machine, is narrow and can sometimes cause discomfort for individuals with claustrophobia or larger body frames.
Pros
- Superior Image Quality
- Versatility
- Reduced Motion Artifacts
Cons
- Claustrophobia and Patient Discomfort
- Limited Accessibility
- Longer Scan Times
Extremity MRI

It is a revolutionary new device that can scan the hands, wrists, elbows, feet, ankles, and knees. MRI operates by using digital images of bones to create 3D models.
This technology helps to accurately evaluate the extremities with great accuracy as well as provide valuable information about anatomical changes or potential medical problems associated with bone abnormalities.
With these advances in imaging technology patient’s healthcare outcomes could be greatly improved. Clinicians are now able to access detailed 3D images that provide them with valuable insight into any issues at hand without having to rely on lengthy wait times.
Pros
- Extremity MRIs all have small footprints.
- They will all give you good images for extremity scanning.
- Cost less than a new standard MRI.
Cons
- They only scan extremities
- You cannot image limbs that are larger than the bore (i.e. the limbs of severely obese patients).
Three General Types of Extremity MRI
- High-field superconductive
- Low-field permanent
- Low-field permanent with limited shoulder capability
3 Tesla MRI
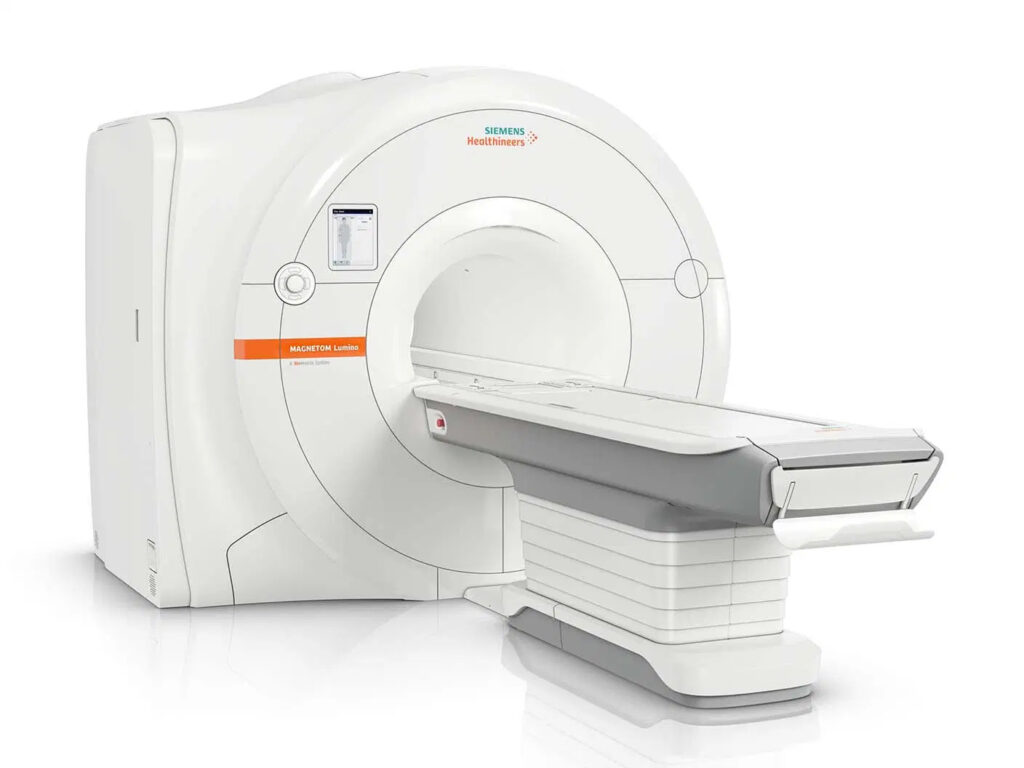
It is the highest peak-field strength scanner, is radiation-free and offers a range of features including faster scan times that makes it an attractive option for imaging.
The higher signal resolution, improved contrast performance, and better tissue separation allow Tesla MRI to produce images with much better detail. It detects attenuation variations in the field more accurately and lowers overall noise levels.
In addition, because the magnetic field provided by 3 Tesla MRI systems is stronger they can provide stronger signals from areas that have weaker properties such as certain types of tissues.
This new device offers higher performance for both clinical diagnosis as well as research studies across many types of medical conditions ranging from neurology to cardiology. With its stronger magnet strength, it can detect subtle changes at greater ranges resulting in more accurate diagnoses or treatments.
Most commonly used for brain, spine, breast, Abdomen /Pelvis, Prostate Glands, and Joints.
Pros
- Fastest Diagnostic Imaging technology
- More Spacious Tube
- Ideal for imaging of small bones and MRIs of breast, neurological, vascular, and musculoskeletal.
- Creates a point of differentiation for the imaging center.
Cons
- It is not well suited for patients with implants.
- For some people, it can cause overheating issues.
- Creates the dielectric effect as a shading artifact
- Abdominal gas can create problematic issues.
- Maintenance costs are higher.
Open Upright MRI
It is a new way to conduct medical imaging. Designed primarily for comfort, offering an open and spacious experience which are usually confined and cramped. All four sides are open. It helps the patient relax while diagnosing illnesses much easier due to improved image quality.
These days more hospitals are turning towards this option as it offers many advantages over other forms of diagnosis making it a better choice for both healthcare providers and patients alike. Open MRIs are perfect for patients with claustrophobia.
It allows the patient to stay in an upright or nearly standing position during their exam, enabling them to view real-time images without having to lie down or remain still.
Pros
- Convenient and Comfortable
- They’re less noisy than traditional Machines.
- Can scan certain body parts easier.
Cons
- It might result in lower-quality images
- Longer scanning times.
In Conclusion,
MRI scans play a crucial role in modern medicine, allowing doctors to diagnose and monitor various health conditions. We have learned about the different types of MRI machines, including closed-bore, open-bore, and upright machines, which cater to various patient needs.
The advancements in MRI technology have revolutionized medical imaging, providing safer and more accurate diagnostic tools. As we continue to progress, we can expect further developments in MRI technology to enhance patient care and improve health outcomes.
The use of MRI technology has allowed doctors to make more informed decisions about patient care, leading to better outcomes for patients. With continued advances in technology, MRI machines will likely become even more advanced in the future.

